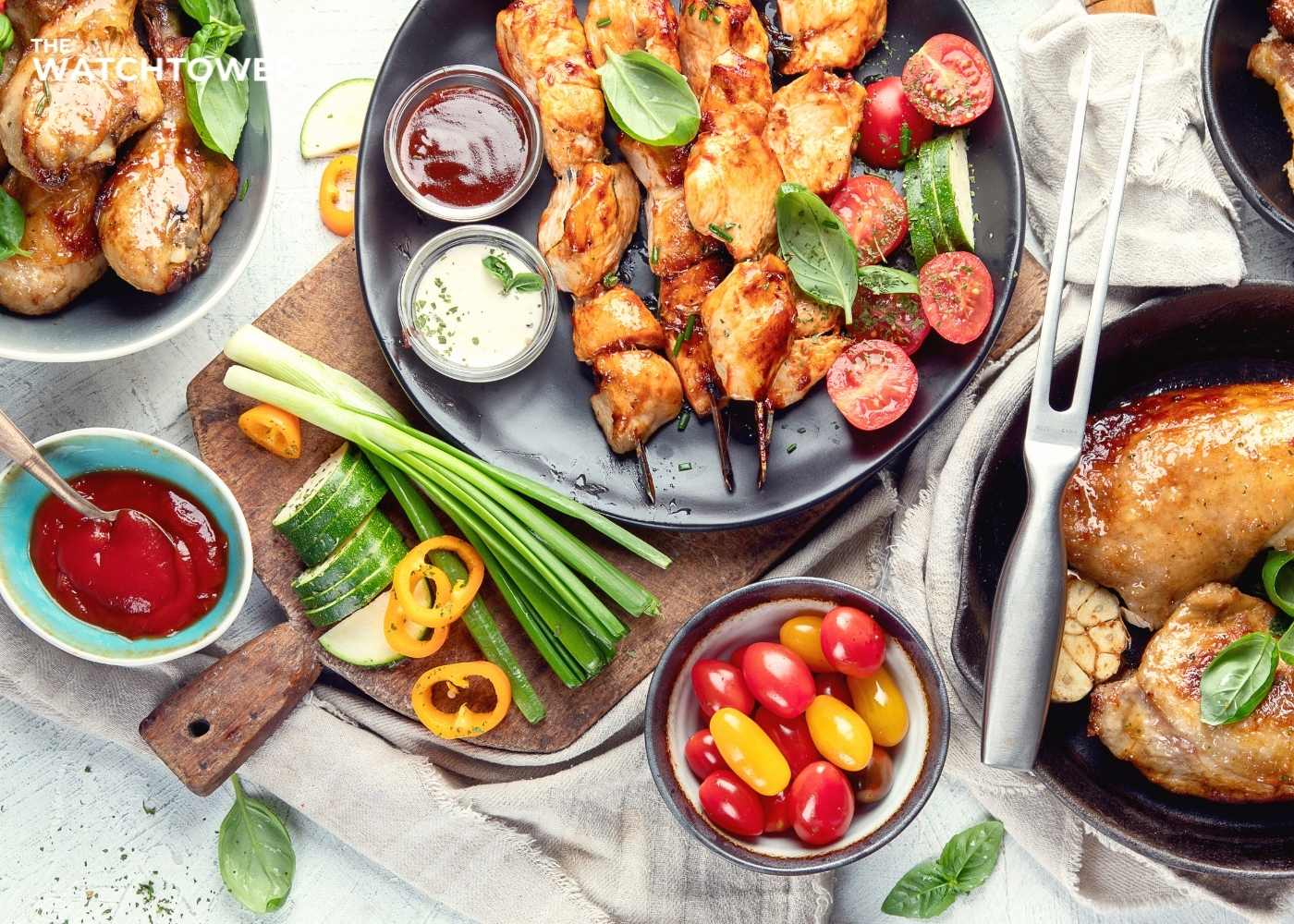

Many individuals are aware that specialists suggest cutting back on their consumption of processed and red meat. These health recommendations are meant to lower people's risk of obesity, heart disease, and other chronic illnesses.
Lean meat and poultry can help someone stay under recommended limits for saturated fat intake and lower their risk of developing chronic diseases. Beef that is at least 90% lean and skinless chicken are healthier options.
This article examines the nutritional profile of lean meats and offers suggestions for selecting the finest ones. It also examines the advantages and disadvantages of lean meat.
What is lean meat?
Lean meat and poultry are varieties and cuts of meat with less fat, such as
Meat and poultry consist of:
- Muscle
- Connective tissue
- Fat
- Bone
Depending on the cut of meat, the muscle in it is made up of around 75% water, 20% protein, and 5% of fat, carbs, and minerals.
However, the muscles and bones of some beef cuts are surrounded by additional fat. In addition, fat can be found in the skin of the chicken.
Compared to other meats, lean meat offers proportionately more protein and less fat.
Gains from lean meat
People can follow the recommendations for health, including limiting saturated fat consumption, by choosing lean meat.
There is proof that consuming more red and processed meat increases the chance of dying, developing heart disease, and developing colorectal cancer. Saturated fat and other substances that can be harmful to health are frequently found in larger concentrations in red and processed meats.
For instance, heme-iron in beef aids in the oxidation of lipids and cholesterol, producing harmful free radicals.
Problems with lean meat
If a person is on a certain diet or healthy meal plan, eating lean meat may not be the best choice. For instance, those who want to follow a ketogenic diet typically select fatty meat over lean meat to enter or sustain ketosis.
While evidence for the safety and efficacy of the keto diet is debatable, avoiding lean meat may assist people on it achieve their goals.
The ideal lean meat to select is
- On beef and poultry, look for labels stating that they are at least 90% lean. Sometimes 93–95 percent lean meat or poultry is available.
- Because grass-fed beef has a better lipid profile and more phytochemicals and antioxidants, it may be healthier to choose it.
- Better fatty acid profiles and advantageous levels of omega-3 can be found in the meat of animals raised by organic standards and given the freedom to forage for food.
- To eliminate the added fat in frying and roasting, people could broil or bake lean meats instead.
The top lean meats to select are listed below:
Lean poultry may be incorporated into a person's diet by eating:
- Skinless chicken and turkey breasts do not contain visible fat.
- Lean ground turkey or chicken.
- Wild game
Lean beef and pork chops include:
- Beef sirloin
- Flat-iron steak
- Bone-in pork loin chops
- Prime cuts of beef with the excess fat cut off
- 95% lean ground beef
Conclusion
Lean meat and poultry choices as part of a balanced diet can lower a person's chance of developing chronic illnesses, including heart disease and early mortality.
Experts suggest choosing meat that is at least 90% lean and trimming off any discernible fat.
Better options include 95 percent lean ground beef, beef sirloin, and skinless chicken. They can aid a person who is adhering to the government's advice that they should consume no more than 10% of their daily calories from saturated fat.
Additionally, avoiding roasting and frying in favour of broiling and baking might help someone consume less fat overall.



















Comments (0)
Write a Comment